Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
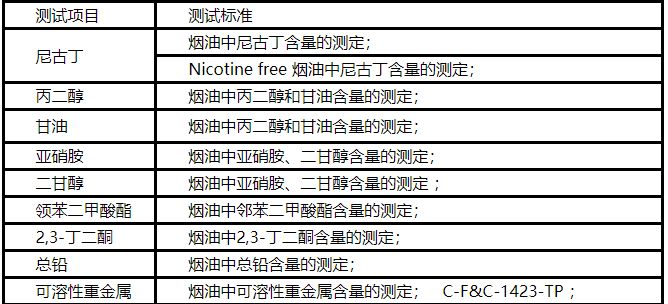
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing
Wireless Communication
Electromagnetic compatibility
Automotive Electronics
Automotive Parts Inspection
Electronic appliances
Chemical Testing
Electronic Cigarette Testing
Reliability testing
Environmental Testing
Battery Testing
Lamp Inspection
Children's toy testing
China Certification
Asia Certification
European Certification
North American Certification
Middle East Certification
Australia Certification
Africa Certification
Registration and filing of wireless communication products
Energy efficiency registration and filing
Registration and filing of chemical products
Management System Standards Training
TRAINING
system certification
Laboratory design and construction
Wireless product testing
BQB testing
Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment
inverter
Power supply for control transformers and built-in control transformers
Medical Electrical Equipment
Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Machinery
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Thermology
Electricity (Safety Regulations for Lighting Appliances)
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Materials
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
Lamp performance testing
Photometer test (IES test)
Photobiosafety testing
Integral Ball Test
(Safety regulations for lighting appliances) Optics
Smart Home Product Testing
Basic testing of household appliances
Structural inspection
Kitchen appliance testing
Beauty and Hair Testing
Household appliance testing
Energy saving testing of household appliances
Switch product inspection
Plug and socket detection
Electronic control device detection
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Physical performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior trim - Environmental testing
Automotive interior and exterior components (non electronic and electrical components) - Material aging performance testing
Automotive interior and exterior decorations (electronic and electrical components) - IP protection
Packaging Material Testing - ISTA 1A-6A
Automotive electronic and electrical components - Electrical performance
Automotive interior and exterior trims - Mechanical performance testing
E-mark certification
EMC Testing
Electrical performance testing
Hazardous substance testing
Consumer Product Chemistry
Ecological textile testing
Inspection of luggage and shoe materials
Food contact material testing
Testing of infant and toddler products
Toy product testing
Mechanical inspection
Temperature, humidity and other weather resistance testing
Noise and Vibration
Environmental consulting services
wastewater
Air and exhaust gas
Soil and sediment
solid waste
Battery performance testing
Portable device battery testing
Portable electric vehicle battery testing
Energy storage battery detection
Child protective packaging testing
battery test
EMC testing
Security testing
Notification, Certification, and Compliance
Consumer Product Testing/Notification Services - Electronic Cigarette Special Section
Chemical testing

One article interpretation: Core requirements of the European Union's Cyberresilience Act CRA
Author.
LCS
Source:
Post time:
2025-12-12
1、 Background of the Act
With the rapid popularization of "smart" devices, IoT terminals, embedded software, and remote data processing systems, ordinary household devices such as smart cameras, refrigerators, toys, wearable devices, and even industrial control systems may become attack targets through network connections and data exchange. Therefore, the formulation of the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) is based on the extreme popularity of digital products, the sharp rise in security risks, insufficient coverage of existing regulations, and the EU's desire to enhance consumer and business trust through unified market rules.
2、 Basic requirements for network security
Firstly, what is a 'product containing digital elements'?
A software or hardware product, as well as a remote data processing solution related to it; Including software or hardware components that are separately launched on the market. Simply put, as long as the product contains software, firmware, chips, or requires connection to the backend system to process data, it is considered a digital product. Even communication modules and software components sold separately are considered.
The safety requirements of the product itself
CRA requires all products with digital elements to be 'default safe' throughout the entire process from design, development to production. When the product is launched, it must not contain known vulnerabilities, and the factory configuration must be a secure configuration; Data transmission and storage need to be encrypted and tamper proof; To prevent unauthorized access, reduce the attack surface, and ensure the sustainable operation of core functions in the event of an attack. At the same time, the product needs to have secure logging capabilities, as well as support for thorough and secure data deletion and migration.
Manufacturer's Vulnerability Management Responsibility
Manufacturers must establish a comprehensive vulnerability management system, including creating a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM), continuously conducting security testing, timely releasing patches, and ensuring that security updates can be automatically pushed; And provide publicly transparent vulnerability information after fixing the vulnerability (which can be delayed if necessary); Establish vulnerability disclosure policies and reporting channels to ensure that users can receive patches quickly and securely. The overall goal is to ensure that the product remains consistently safe throughout its entire lifecycle.
3、 Scope of application
As long as the purpose of the product is to connect data with devices or networks. Almost all are applicable to CRA.
Specifically, it can be divided into important products and key products
Important products: network management systems, standalone/embedded browsers, password managers, network management systems, boot managers, operating systems, various software products, security related microprocessors/controllers, routers, switches, firewalls, intrusion detection and defense systems, etc.
Key products: Hardware devices with security boxes, smart meter gateways, smart cards or similar devices, security elements, other devices used for advanced security purposes, including devices used for secure encryption processing.
4、 Punishment
According to the Cybersecurity Resilience Act, for violating companies, a maximum penalty of 2.5% of the global annual revenue for the previous fiscal year or an administrative fine of 15 million euros can be imposed. Providing incorrect, incomplete, or misleading information to notified bodies and market supervision agencies may result in a maximum penalty of 1% of the global annual revenue for the previous fiscal year, or an administrative fine of 5 million euros.
5、 Effective time
The notification obligation of qualified assessment institutions will take effect from June 11, 2026.
The manufacturer's obligation to report security incidents will be implemented from September 11, 2026: the obligation for manufacturers to report when they discover vulnerabilities or serious security incidents in their products that have been actively exploited. Manufacturers are required to report vulnerabilities or security incidents to CSIRT and ENISA within specific time periods (such as 24 hours, 72 hours, 14 days, etc.) and provide detailed event information, impact assessments, remediation measures, etc.
All other regulations will come into effect from December 11, 2027.
6、 The difference between the Network Resilience Act (CRA) and the EN 18031 standard:
CRA: For all products with digital elements, including hardware, software, embedded systems, IoT devices, etc. Its purpose is to ensure the network security of these products from design to lifecycle management, requiring manufacturers to consider network security in product design and production processes, and provide remediation measures for known vulnerabilities.
EN 18031: It is a European standard for specific fields, mainly focusing on developing network security requirements for networked wireless devices (such as smart home devices, wireless communication devices, etc.).
Related articles
New articles
Media Center
Latest News
Contact Us


National 24-hour service hotline
400-116-2629
Group Headquarters
E-mail: webmaster@lcs-cert.com
Address: Shenzhen City, Baoan District, Shajing Street, Nga side of the school of Wei Juji Industrial Park, Building A 1 ~ 2 floor, Building C 3 floor
Contact Us
National 24-hour service hotline
Address:Juji Industrial Park, Xueziwei, Ngabian, Shajing Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen Building A 1~2F, Building C 3F

WeChat public number
Share industry dry goods

WeChat consultation
Please note consulting services

Follow Jitterbug

Mobile website
di complaint mailbox: customer.complaint@lcs-cert.com complaint telephone tel: 18126445450 certificate report verification of authenticity mailbox: verification@lcs-cert.com


 Wireless and communication detection
Wireless and communication detection
 Mobile communication product certification
Mobile communication product certification
 Bluetooth BQB Product Certification
Bluetooth BQB Product Certification
 FM/AM Product Certification
FM/AM Product Certification
 WiFi Product Certification
WiFi Product Certification
 Wireless charging product certification
Wireless charging product certification
 Interphone product certification
Interphone product certification
 Base station certification
Base station certification
 SAR testing
SAR testing
 Receiver Product Certification
Receiver Product Certification
 5G NR Product Certification
5G NR Product Certification
 UWB Product Certification
UWB Product Certification
 Internet of Things authentication
Internet of Things authentication
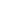
 Automotive Electronics EMC Testing
Automotive Electronics EMC Testing
 EMC rectification
EMC rectification
 EMC
EMC
 Electrical performance testing
Electrical performance testing
 EMS testing - radiation anti-interference testing system (including radar waves)
EMS testing - radiation anti-interference testing system (including radar waves)
 EMS Testing - Electrostatic Discharge
EMS Testing - Electrostatic Discharge
 EMS Test - Transient Conducted Immunity Test
EMS Test - Transient Conducted Immunity Test
 EMS Testing - Portable Transmitter Immunity
EMS Testing - Portable Transmitter Immunity
 EMS Test - High Current Injection (BCI) Test
EMS Test - High Current Injection (BCI) Test
 EMS test - low-frequency magnetic field anti-interference test
EMS test - low-frequency magnetic field anti-interference test
 EMI Testing - Transient Conducted Emissions Testing System
EMI Testing - Transient Conducted Emissions Testing System
 EMI testing - low-frequency magnetic field emission
EMI testing - low-frequency magnetic field emission
 EMI Test - Radiation Emission Test
EMI Test - Radiation Emission Test
 EMI Test - Conducted Emissions Test
EMI Test - Conducted Emissions Test
 Automotive Electronic Testing
Automotive Electronic Testing
 Automotive ELV&VOC
Automotive ELV&VOC
 Reliability testing
Reliability testing
 Temperature shock test
Temperature shock test
 Vibration testing
Vibration testing
 Instrument panel/instrument panel three comprehensive vibration test
Instrument panel/instrument panel three comprehensive vibration test
 Comprehensive vibration test of door inner panel III
Comprehensive vibration test of door inner panel III
 Sunvisor Three Comprehensive Vibration Test
Sunvisor Three Comprehensive Vibration Test
 Spoiler Three Comprehensive Vibration Test
Spoiler Three Comprehensive Vibration Test
 Three comprehensive vibration tests of car front and rear bumpers
Three comprehensive vibration tests of car front and rear bumpers
 Three comprehensive vibration tests for lamp housing/lampshade
Three comprehensive vibration tests for lamp housing/lampshade
 Comprehensive vibration test of outer circumference three
Comprehensive vibration test of outer circumference three
 Automotive metal material testing
Automotive metal material testing
 Performance testing of automotive lighting fixtures
Performance testing of automotive lighting fixtures
 Rapid temperature change test
Rapid temperature change test
 Vibration
Vibration
 Common issues with vibration testing
Common issues with vibration testing
 Common issues with fatigue testing
Common issues with fatigue testing
 Common issues with high and low temperature testing
Common issues with high and low temperature testing
 Conducted Interference (CE) - Suzhou Lixun Standard
Conducted Interference (CE) - Suzhou Lixun Standard
 Electromagnetic Radiation Tolerance Test (RS) - Suzhou LCS Standard
Electromagnetic Radiation Tolerance Test (RS) - Suzhou LCS Standard
 Electrical Fast Pulse Withstand Test (EFT) - Suzhou LCS Standard
Electrical Fast Pulse Withstand Test (EFT) - Suzhou LCS Standard
 Voltage flicker test - Suzhou LCS standard
Voltage flicker test - Suzhou LCS standard
 Household appliance product testing
Household appliance product testing
 Electrical accessory product testing
Electrical accessory product testing
 Household appliance testing
Household appliance testing
 Consumer Product Testing Services - WEEE Chapter
Consumer Product Testing Services - WEEE Chapter
 Ecological textile testing
Ecological textile testing
 Leather Footwear Inspection
Leather Footwear Inspection
 Food contact material testing
Food contact material testing
 Testing of toys and baby products
Testing of toys and baby products
 Hazardous substance testing
Hazardous substance testing
 Electronic cigarette detection
Electronic cigarette detection
 Other tests - pencil hardness test
Other tests - pencil hardness test
 Mechanical testing - Packaging compression test
Mechanical testing - Packaging compression test
 Climate environment testing - Xenon lamp aging test
Climate environment testing - Xenon lamp aging test
 Water Quality Testing
Water Quality Testing
 environment detection
environment detection
 Power storage battery testing and certification
Power storage battery testing and certification
 Consumer Electronics Battery Testing and Certification
Consumer Electronics Battery Testing and Certification
 Battery
Battery
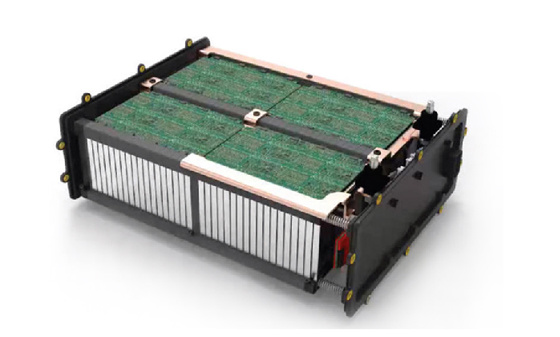 Light electric vehicle batteries
Light electric vehicle batteries
 Energy storage battery
Energy storage battery
 Portable battery
Portable battery
 Battery testing
Battery testing
 battery test
battery test
 COI Index Test for Medical Indoor Lighting
COI Index Test for Medical Indoor Lighting
 Lamp safety inspection
Lamp safety inspection
 Luminaire energy efficiency testing
Luminaire energy efficiency testing
 EMC testing of lighting fixtures
EMC testing of lighting fixtures
 Integral Ball Laboratory
Integral Ball Laboratory
 Photobiology Experiment
Photobiology Experiment
 Light distribution test
Light distribution test
 Lamp aging test
Lamp aging test
 Lamp IP waterproof
Lamp IP waterproof
 Lamp performance testing
Lamp performance testing
 Lamp reliability testing
Lamp reliability testing
 Testing standards for toy products
Testing standards for toy products
 China's "national promotion" RoHS certification
China's "national promotion" RoHS certification
 China Energy Efficiency Label Certification
China Energy Efficiency Label Certification
 China Energy Conservation Certification
China Energy Conservation Certification
 China CQC Certification
China CQC Certification
 Tmall JD Quality Inspection Report
Tmall JD Quality Inspection Report
 China SRRC Certification
China SRRC Certification
 Taiwan BSMI certification
Taiwan BSMI certification
 Taiwan NCC certification
Taiwan NCC certification
 China CCC Compulsory Certification
China CCC Compulsory Certification
 KC certification
KC certification
 KUCAS Certification in Kuwait
KUCAS Certification in Kuwait
 Vietnam COC certification
Vietnam COC certification
 Singapore PSB certification
Singapore PSB certification
 Iraq COC Certification
Iraq COC Certification
 Qatar COC Certification
Qatar COC Certification
 Iran COI certification
Iran COI certification
 GCC Certification for Gulf Seven Countries
GCC Certification for Gulf Seven Countries
 IMDA certification
IMDA certification
 VCCI Certification in Japan
VCCI Certification in Japan
 JATE certification in Japan
JATE certification in Japan
 PSE certification
PSE certification
 BIS certification
BIS certification
 Japanese TELEC certification
Japanese TELEC certification
 GOST certification in Russia
GOST certification in Russia
 Russian EAC certification
Russian EAC certification
 Northern Ireland UKNI logo
Northern Ireland UKNI logo
 Electrical ENEC certification
Electrical ENEC certification
 European D-MARK certification
European D-MARK certification
 Türkiye BTK certification
Türkiye BTK certification
 TSE certification in Türkiye
TSE certification in Türkiye
 CE certification in Türkiye
CE certification in Türkiye
 RED certification
RED certification
 German TUV-SUD certification
German TUV-SUD certification
 REACH certification
REACH certification
 German GS certification
German GS certification
 EU E-Mark certification
EU E-Mark certification
 Ecuador VOC certification
Ecuador VOC certification
 Mexico NOM certification
Mexico NOM certification
 IRAM certification
IRAM certification
 CPSC Certification in the United States
CPSC Certification in the United States
 ASTM certification
ASTM certification
 FDA certification
FDA certification
 CEC certification
CEC certification
 ETL certification
ETL certification
 ul certification
ul certification
 IC certification
IC certification
 Energy Star
Energy Star
 FCC Certification in the United States
FCC Certification in the United States


 UL, ETL, CSA, MET, TUV certification in the United States
UL, ETL, CSA, MET, TUV certification in the United States
 ASTM certification
ASTM certification
 Saudi SABER certification
Saudi SABER certification
 Saudi SABER Certification Gulf Seven GCC Certification
Saudi SABER Certification Gulf Seven GCC Certification
 Iran COI certification
Iran COI certification
 Qatar COC Certification
Qatar COC Certification
 Iran COI certification
Iran COI certification
 Qatar COC Certification
Qatar COC Certification
 Iraq COC Certification
Iraq COC Certification
 Saudi EER Energy Efficiency Certification
Saudi EER Energy Efficiency Certification
 Saudi SABER certification
Saudi SABER certification
 Saudi EER Energy Efficiency Certification
Saudi EER Energy Efficiency Certification
 Algeria PCA certification
Algeria PCA certification
 PVOC certification
PVOC certification
 New Zealand IC-F testing
New Zealand IC-F testing
 VEET certification
VEET certification
 LCP certification
LCP certification
 GEMS certification
GEMS certification
 RCM certification
RCM certification
 C-Tick certification
C-Tick certification
 SAA certification
SAA certification
 Gabon COC certification
Gabon COC certification
 Algeria COC certification
Algeria COC certification
 Ethiopian VOC and COC certification
Ethiopian VOC and COC certification
 Mauritius VOC certification
Mauritius VOC certification
 Ghana COC certification
Ghana COC certification
 COC certification in Burundi
COC certification in Burundi
 Zambia COC certification
Zambia COC certification
 Botswana COC Certification
Botswana COC Certification
 Uganda PVOC certification
Uganda PVOC certification
 SABS certification in South Africa
SABS certification in South Africa
 South African LOA certification
South African LOA certification
 Zimbabwe CBCA Certification
Zimbabwe CBCA Certification
 Nigeria SONCAP certification
Nigeria SONCAP certification
 Kenya PVOC certification
Kenya PVOC certification
 African COC certification
African COC certification
 WEEE
WEEE
 Bluetooth BQB certification
Bluetooth BQB certification
 IECEE registration
IECEE registration
 MHRA registration in the UK
MHRA registration in the UK
 Management system training
Management system training
 Laboratory technical training
Laboratory technical training
 Laboratory Process Consulting
Laboratory Process Consulting
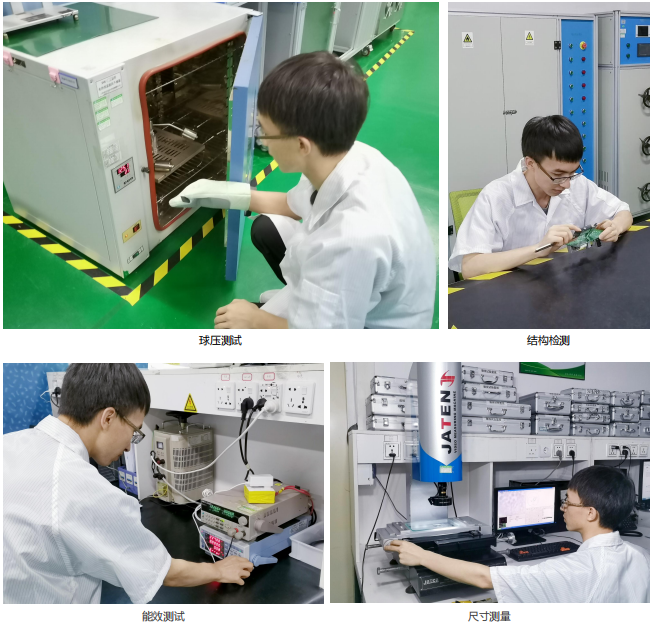 Laboratory decoration construction
Laboratory decoration construction




 WeChat Inquiry
WeChat Inquiry